Spotlight What Matters Most in Your Customer Conversations
Spotlight Summaries are here to shine a light on key trends in your conversations. This new feature analyses multiple interactions
Text classification techniques can be used by contact centres to enhance reporting, improve auto responses, and reduce agent handling times. In this post we look at how text classification works and what the best use of text classification techniques is in the customer contact centre.

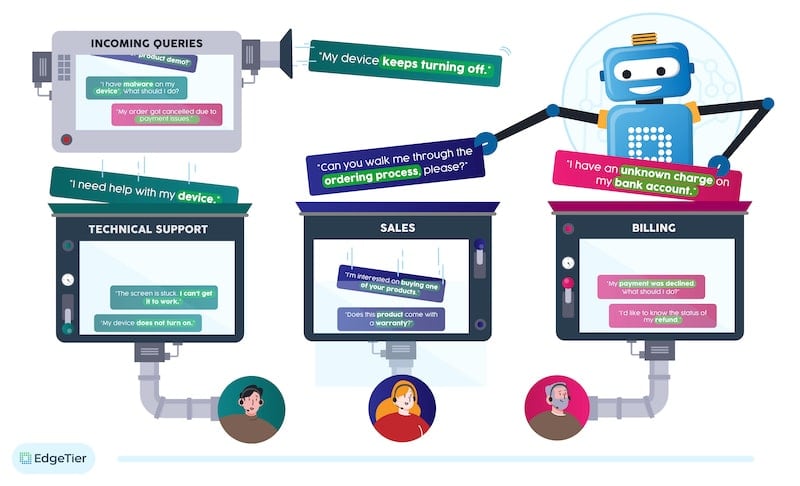
When new queries arrive at the contact centre, machine learning can examine the contents of the query, and determine “what is this customer talking about”. The application of AI in this manner, as with chatbots, is called “text classification”, that is the assignment of different bodies of text into separate labelled buckets. For example, an AI system could be taught that the phrase “I no longer will be going on holidays” as a “cancellation” query for a travel company.
Contact centres can use text classification results for a variety of applications, including:
The simplest method to achieve automated text classification is keyword detection. For example, a contact centre could label all queries with the word ‘cancel’ in them as “cancellation queries”. This method is intuitive, and the first idea that people have when they want to “detect what is happened”.
While fast to set up, and easily understandable, keyword-detection approaches are difficult to maintain, sensitive to slang or misspelled words, typically very challenging to expand to multiple languages, and will not achieve very high accuracy without extensive manual work. For example, the queries “please cancel my booking” and “I don’t want to cancel my booking” both have the terms “cancel” and “cancel my booking” in them.

While not recommended for long-term use over many categories, keyword detection has it’s place to define a “baseline performance”, and failing the availability of a more accurate approach, it can be a useful starting point to demonstrate value.
Artificial intelligence (AI) text classification techniques provide more flexible approaches that can address the shortfalls of the keyword-based approach. AI approaches use statistical language models to classify pieces of text. These models can extrapolate from examples to take word order into account, incorporate slang, counter for common misspellings, and take the context of words into account when making predictions.
AI systems “learn by example”, so most text-classification systems will require a dataset of “training” or “example” data to start off with. The early approaches required many hundreds or even thousands of training samples, typically manually labelled, to produce accurate models. Thankfully, advances in training techniques have dramatically reduced the volumes of training data required (from thousands to tens). As such, AI text-classification models can be fine-tuned to your brand’s and customer’s individual terminology and issues.
Natural-language-based text classification techniques have improved in accuracy over recent years, with accuracies of 95+% obtainable by experienced practitioners. Modern text-classification systems make extensive use of word and sentence embeddings and can work in multilingual environments.
A huge advance in machine learning techniques that has driven a step-change in text classification accuracy since 2015 has been the invention of “transfer learning” for NLP tasks. Previously, data samples would learn the statistical patterns of word appearances for sentences that trigger text-classification from manually labelled datasets. This was the “bag of words” approach, which used maths operations to identify common and uncommon words for topics of interest. Each time a new model was being built, the data scientist started from scratch with a new data set.
In transfer-learning approaches, a single, much larger model is trained on a gigantic volume of text (for example, the entirety of Wikipedia in English). These models learn how words appear together and their typical order of appearance, for vast quantities of language use. The models are computationally expensive to train, taking many machines multiple days to complete and are often completed by large companies or research institutes (Google / Facebook / Stanford / Microsoft). However, once trained, the resulting model output can be integrated into new text-classification models (i.e. the core language information is “transferred”).
Now, when building a new text-classification model, a data scientist can begin by downloading a pre-existing pre-trained language model, and then layer the domain-specific classification task on top. This approach dramatically increases prediction accuracy with fewer labelled samples, speeds up the development process, and “injects” the statistical learnings from much larger bodies of text into the model workings!
Text classification is a perfect mechanism to “dip your toe” in the machine learning world for customer contact centres, and can be used to show value almost immediately. The classification of received text surveys and inbound customer queries can be performed offline before doing any system integrations, and the results can be used to inform quality improvement initiatives with quantitative “voice of the customer” data.
The key steps to successful application of automated tagging is to focus on the right customer topics and not overreach. The best outcomes will be for customer service topics that are:
Spotlight Summaries are here to shine a light on key trends in your conversations. This new feature analyses multiple interactions
We’ve just added confusion detection to our emotion analysis tools. Now, you can easily spot when customers are confused, allowing
Discover how EdgeTier’s latest AI-powered updates can optimise your contact centre, including anomaly detection summaries, agent QA, and custom charts.
"EdgeTier is really shining when it comes to responsible gambling. We can proactively track critical issues and take actions, reducing human error."
"It has reduced the time for the quality assurance process as it provides clear data and a very robust direction on where to look and what matters the most."
"The anomaly feature is a game changer for us. It’s highly accurate and has helped us identify customer issues, agent errors, and even fraud that would have taken us longer to catch."



Let us help your company go from reactive to proactive customer support.
Unlock AI Insights